~~~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
|
If it acts of a new entity or not, it is necessary to make a functional cutting of it to identify and treat the functions on a hierarchical basis in order to look for the failures*. The research of the functions is carried out by studying the connection between the product, the process or the service with its environment. It is a question of identifying created links, of defining the constraints and of organizing the existing elements
For a product, a means of production or software: diagram of functional analysis.
Example:
|
|
~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
Functional decomposition |
~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
|
Function :
F1 : to be visible and locatable under all conditions
F2 : to isolate the user from the climatic conditions
F3 : easily maintained
F4 : to be able to be repaired
F5 : easily installed and uninstalled
F6 : is able to be organised |
|
|
~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
|
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
|
|
| ~~~~~~~~~~~~ |
| |
| |
|
Constraints :
C1 : adaptable
C2 : in conformity with normal standards
C3 : has a minimum volume
C4 : is in style
C5 : has forms and is in materials ensuring the safety of the skier
C6 : respects the fabrics |
|
| |
|
Figure 2 : Diagramme d'analyse fonctionnelle, (d'après Exprimer le besoin - AFAV. Afnor, 1989).
|
|
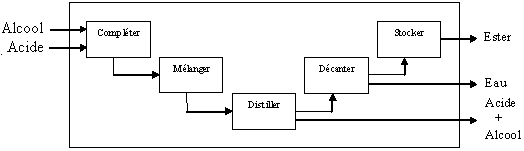
For a process: traditional synoptic diagram or of logical the boxes type. Example: |
| |
|
| |
Figure 3 : Diagramme d'analyse fonctionnelle, (d'après Exprimer le besoin - AFAV. Afnor, 1989). |
|
| |
| |
| |
|
| |
| |